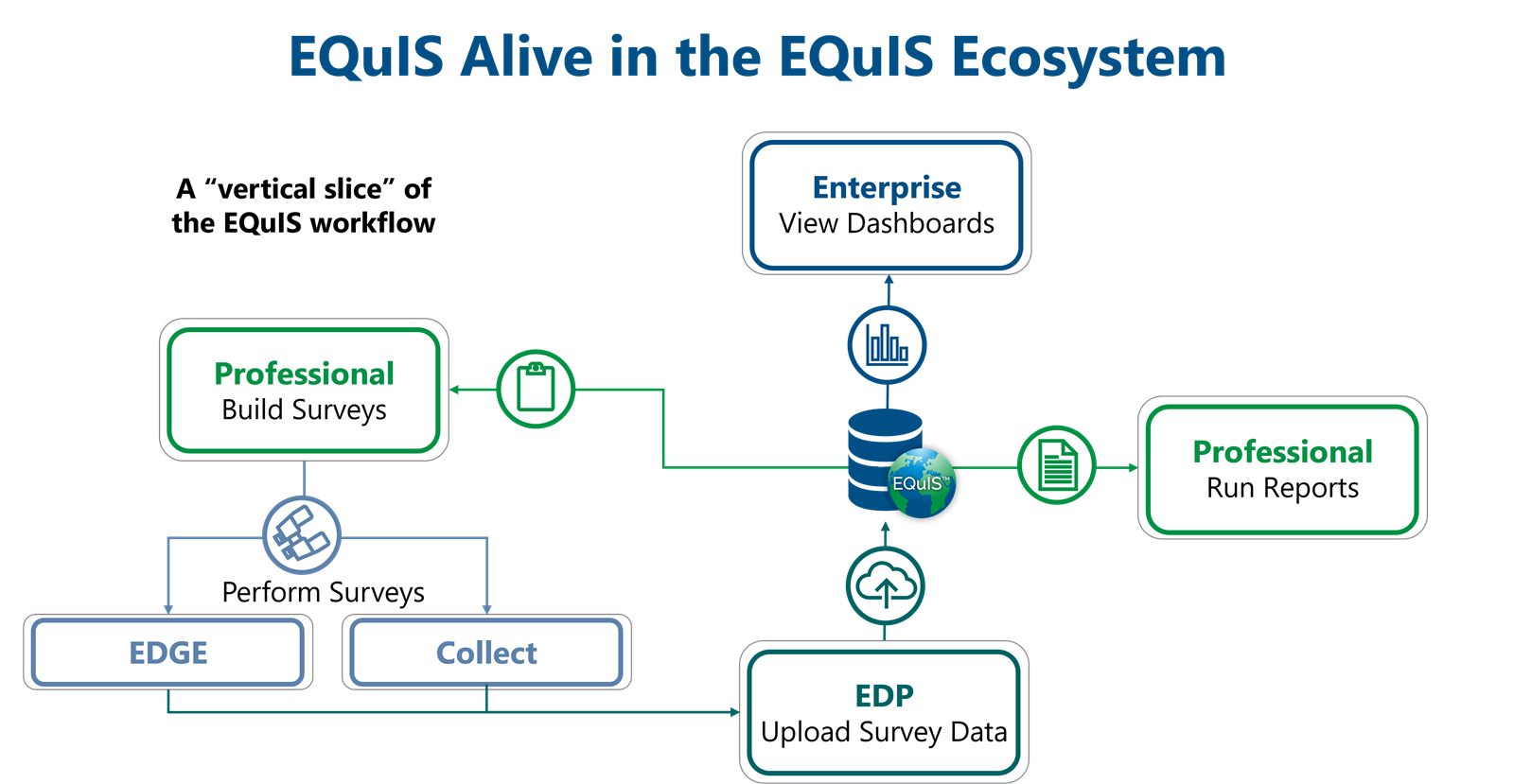
Overview
EQuIS Alive extends EQuIS to manage survey, ecological, biological, and taxonomy data. Users can build and use surveys to collect and manage this data. Alive integrates with other EQuIS applications for enhanced biological data analysis and assists with habitat assessment and inventory management of invasive, indigenous, and protected species. Alive combines with other EQuIS applications for easy and efficient data consumption and visualization.
Watch the Introduction to EQuIS Alive Office Hour recording for an overview of Alive.
Watch the Visualizing Alive Data in Enterprise Office Hour recording for a demonstration of using and sharing Alive data.
Alive Structure
EQuIS Alive differs from the normal analytical sample structure within EQuIS.

Alive Surveys
EQuIS Alive is built around the concept of performing surveys. Surveys are a repeatable series of Observations that take place over one or more specifically-defined Areas. They may be defined for any single taxonomy or entire group of organisms, such as birds, frogs, fish, trees, etc. Surveys may also include ambient weather and habitat observations or conditions as well as data pertaining to one or more species of plant or animal. They are similar to “Tasks” in the standard EQuIS Schema.
Some potential survey types are:
•Species Inventory and Monitoring
•Invasive Species
•Indigenous Species
•Protected Species
•Habitat Assessment
•Vegetation Management
•Clearing and Relocation
•Re-vegetation
•Ecological Observations
•Date and Time
•Place
•Species
See the Create an Alive Survey article for further details.
Alive Observations
Observations are sets of information collected about a target species during a Survey. Observations are similar to “Results” in the standard EQuIS Schema. Examples of observations are:
•Evidence of mice (droppings) but no specimens seen
•Red-legged Thrush seen at ~10 m in a tree
•> 20 Bletia purpurea estimated per square meter
Samples can be linked to Alive observations. Read the Linking Alive Samples to Observations article to learn more.
Alive Subfacilities (Areas)
Because surveys can be performed over large spatial areas, surveys are tied to subfacilities in EQuIS, instead of locations. The Alive formats (i.e., surveys) require that the subfacility be populated (DT_SURVEY.SUBFACILITY_CODE lookup column links to DT_SUBFACILITY.SUBFACILITY_CODE). Optionally, survey observations may also be associated with subfacilities (DT_SURVEY_OBSERV.SUBFACILITY_CODE).
Why subfacilities and not locations? A location traditionally represents a single point in EQuIS, such as a monitoring well or weather station. Subfacilities typically address areas rather than points, though they can still represent a point. Subfacilities can be used for sections of a facility, lakes, parts of a lake, fields, streams, a forest, etc.
Additionally, given the different nature of EQuIS Alive surveys, the DT_COORDINATE table (as a child of DT_LOCATION) may not be a good fit for the spatial data associated with surveys and observations. Therefore, the DT_SPATIAL_EXTENT table was introduced to support the different spatial data needs of surveys and observations. For further details on the DT_SPATIAL_EXTENT table, please refer to the help article Spatial Data Tables.
Alive Taxonomy
Observations made during a survey typically revolve around some species of flora or fauna. This list of species is contained in a hierarchical table, RT_TAXONOMY. The RT_TAXONOMY table is configured so that the species can be grouped together in a logical fashion.
This hierarchy of grouping can be as complex as the full taxonomical rankings:
•Life
▪Eukaryota
▪Animalia
oChordata
•Aves
▪Passeriformes
▪Passeroidea
▪Passeridae
opasser domesticus (House Sparrow)
▪Plantae
oetc...
or as a simple flat list of species:
•Passer ammondendri
•Passer domesticus
•Passer italiae
It is recommended, and the most usable, to create a table structure that falls somewhere in between these two extremes. An example structure might be:
•Animalia
•Birds
▪Passer domesticus
▪etc...
•Fish
▪etc...
•etc...
•Plantas
•Trees
▪etc...
•etc...
•etc...
Note: By setting up groups of species in the RT_TAXONOMY table, there is no need to set them up in the RT_GROUP table. Any level of the taxonomy structure can be associated with a particular survey, and that survey will include any child records with that RT_TAXONOMY.TAXONOMY_CODE. See the help article Create an Alive Survey for further detail. Use the Alive-refvals Format to establish taxonomy reference values. |
Warning: RT_TAXONOMY.TAXONOMY_CODE and RT_TAXONOMY.PARENT_CODE should be unique names. For example, TAXONOMY_CODE should not have a PARENT_CODE with the same name. Doing so may result in unexpected behavior, such as being unable to create or export Alive surveys. |