The EQuIS remap tool facilitates management of reference and lookup value synonyms on both import and export of data while maintaining the single core set of reference values defined in the EQuIS database.
For example, you may have RT_MATRIX.MATRIX_CODE = SO for soil in your EQuIS database, but be required to report using MATRIX_CODE = SOIL to comply with the specific criteria of a regulatory agency or project. The remap tool is available in EDP for editing data prior to loading, as well as in EQuIS Professional for updating existing data or remapping report output.
Note: EQuIS offers several additional options for handling analyte name synonyms, specifically the RT_MTH_ANL_GROUP_MEMBER.CHEMICAL_NAME field and the RT_ANALYTE_VAR table. |
To get started with remapping, first populate the tables to define remap sets.
To use a remap set to replace values, do the following:
1.Click the Find ![]() button on the Home ribbon.
button on the Home ribbon.
2.In the Find and Replace window, click the Remap tab.
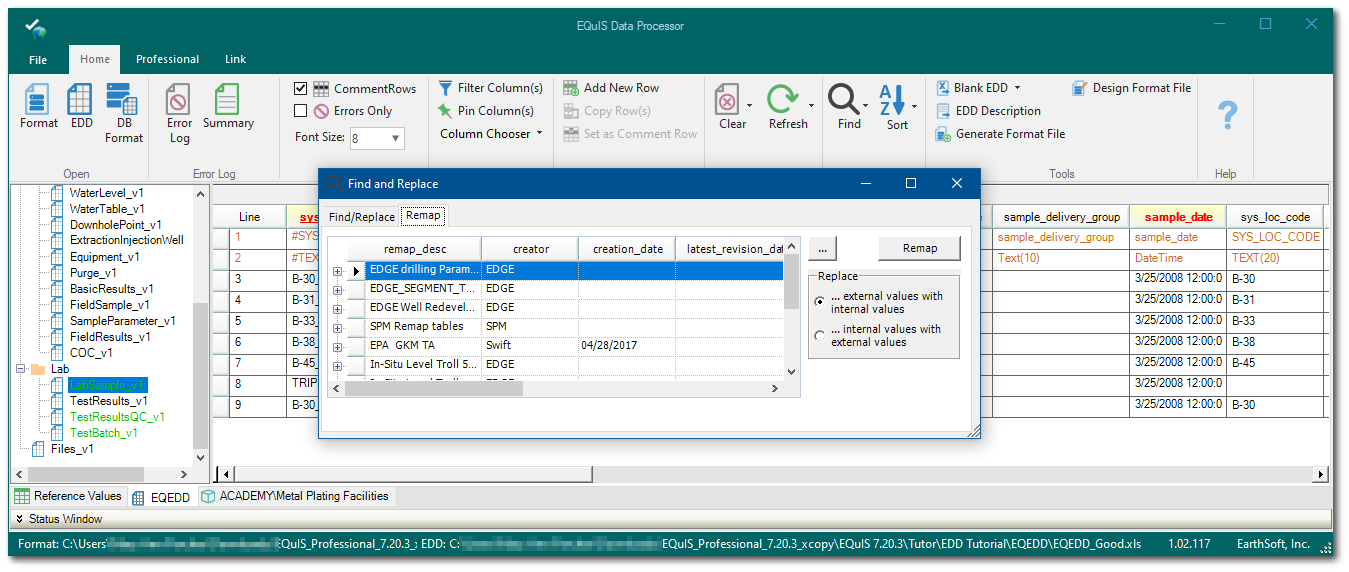
3.If nothing is displayed in the list, EDP does not have a live connection to the database (i.e., EDP Standalone). In this case, click the "..." button to browse for a *.xml file (saved from the EQuIS Professional workspace). See the Remap Sets - Saving to an External File article to learn how to export a remap file.
4.Select the row to use for the remap set (expand the row to see what values will be replaced).
5.Select which replacement option to use (EXTERNAL_VALUE replaced by INTERNAL_VALUE or INTERNAL_VALUE replaced by EXTERNAL_VALUE).
6.Click the Remap button to execute the remap.
Warning: Remapping applies to all tables or sections allowed in the remap set, regardless of whether the table/section is open while the remap is executed. It is impossible to undo a remap. The internal-external replace order can be reversed, but this will not work if there are many-to-one mappings. |